Solid-state batteries have become one of the most talked-about technologies in the energy-storage world. Although the concept is not brand new, recent breakthroughs in materials and manufacturing have pushed solid-state batteries closer to real commercial use.
This article provides a clear, practical, and engineering-friendly explanation of solid-state batteries—from how they work to where they are heading.
What Exactly Is a Solid-State Battery?
At its core, a solid-state battery is similar to a lithium-ion battery in structure. It still uses an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte that allows lithium ions to travel between the two electrodes. However, the electrolyte is not a liquid or gel. It is a solid material—often ceramic, polymer, glass, or a sulfide-based compound.
This difference seems subtle, but it fundamentally changes how the battery behaves.
Components of a Solid-State Battery
- Anode: Can be made of traditional graphite, but many R&D teams aim to pair solid electrolytes with lithium metal anodes for higher capacity.
- Cathode: Similar to those used in Li-ion batteries (NCM, LFP, etc.), though structure and manufacturing methods may differ.
- Solid Electrolyte: The defining component. It can be rigid or flexible, depending on the material type.
- Separator (sometimes integrated): In many designs, the solid electrolyte also functions as the separator.
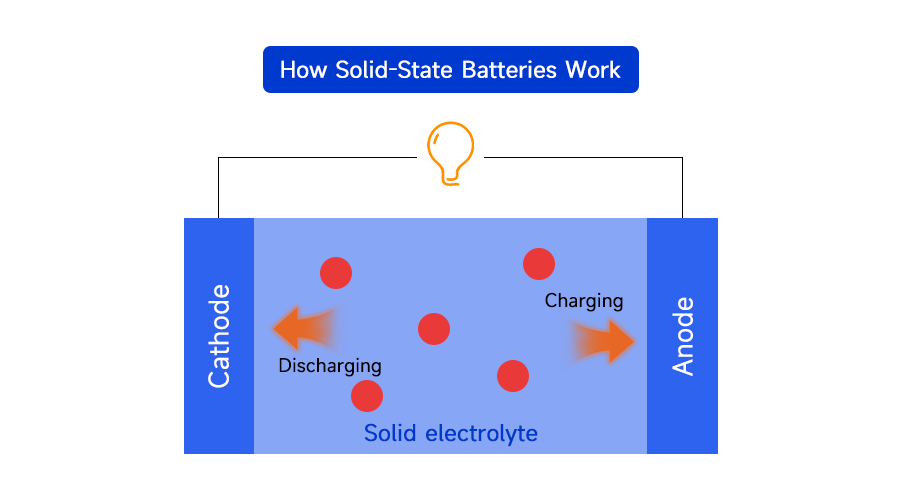
How Solid-State Batteries Work
Ion movement is still the core mechanism. When a device is operating, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode through the solid electrolyte. During charging, the ions flow in the opposite direction.
In liquid-electrolyte batteries, ions move through an organic electrolyte soaked into a porous separator. The liquid is highly conductive but also flammable. In solid-state batteries, ions travel through a solid, which is non-flammable and structurally stable. This stability reduces the risk of leakage, thermal runaway, and dendrite-induced short circuits.
However, ions do not move as freely in solids as they do in liquids, which introduces engineering challenges—one reason why mass production remains difficult.
Benefits of Solid-State Batteries for OEMs and Industrial Applications
- Higher Energy Density: Solid electrolytes make it possible to pair cathodes with a lithium metal anode, dramatically increasing the amount of energy stored in the same physical space.
- Enhanced Safety and Thermal Stability: Solid-state batteries remove the flammable organic liquid used by common batteries. This means fewer fire risks.
- Wider Operating Temperature Range: Solid electrolytes can maintain performance under harsher temperature conditions compared to liquid electrolytes.
- Longer Cycle Life and Lower Maintenance: A stable solid electrolyte reduces internal chemical reactions that cause battery aging. This means fewer replacements, lower maintenance costs, and longer product life cycles.
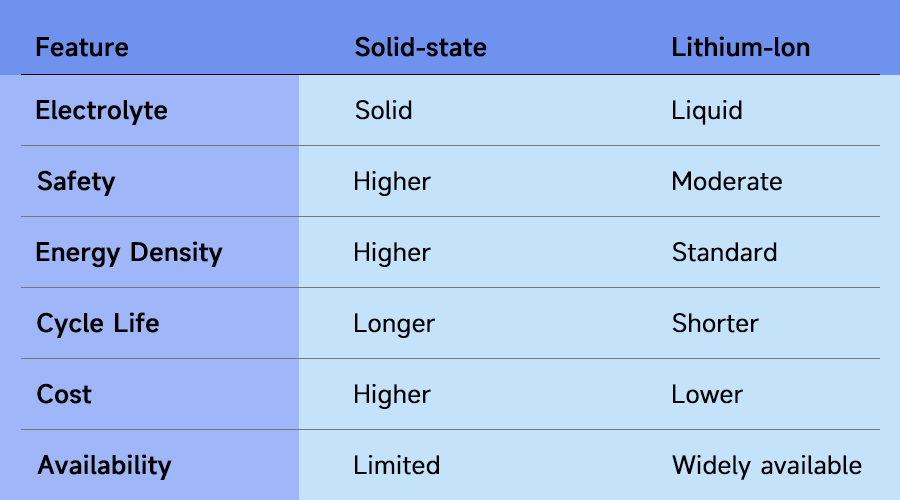
Solid-State vs. Traditional Lithium-Ion Batteries
Performance
Solid-state batteries can surpass traditional Li-ion by 30–50% or more. Its lower degradation leads to longer usable life.
Manufacturing Differences
Solid-state batteries are much harder to manufacture. Producing solid-state batteries at scale is complex.
Traditional Li-ion manufacturing, on the other hand, is decades ahead, with highly optimized processes and an established global supply chain.
Cost
At present, solid-state batteries are often too costly for mass consumer applications. Li-ion batteries are more affordable.
Solid-State Battery VS Li-ion Battery Table
Main Application Areas
- Electric Vehicles: Automotive companies are investing heavily in solid-state R&D. Higher energy density and enhanced safety are major selling points.
- Industrial IoT Sensors and Smart Metering: Long operational life and strong temperature tolerance make solid-state batteries ideal for sensors installed in remote or harsh environments, such as smart water meters, gas detectors, and asset tracking devices.
- Medical Devices: Medical implants, wearable health monitors, and portable diagnostic equipment require these extremely reliable batteries.
- Aerospace and Military Systems: These fields prioritize reliability under extreme conditions. Solid-state’s robustness, safety, and temperature tolerance align closely with those needs.
- High-Performance Consumer Electronics: Small but powerful devices—AR/VR headsets, next-generation wearables, miniaturized computing devices—could adopt solid-state technology once costs drop.
Should Your Company Switch to Solid-State Batteries?
Solid-state batteries are undoubtedly a good technology. But to switch to these batteries, you need to consider the budget and supply chain. Its cost is still high, and the suppliers are limited.
For now, you can still use other batteries as alternatives, such as, Li-ion battery, Lipo battery, LiFePO4 battery, NiMH battery, etc.. If you have battery needs, you may reach out to PKCell for a wholesale price for the battery you need, for PKCell has 20 years battery manufacture experience and provide high performace and reliable rechargeable batteries and offer professional custom battery service.
Contact PKCell for Bulk Batteries
Conclusion
Solid-state batteries are not just a theoretical innovation. They represent one of the most promising directions for next-generation energy storage.
For now, the technology may not replace traditional lithium-ion in all applications, but it is steadily moving closer to real-world deployment.
FAQs about Solid-State Battery
1. What is a solid-state battery?
A solid-state battery uses a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one. This makes it safer and capable of higher energy density than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
2. Why are solid-state batteries considered safer?
They do not contain flammable liquid electrolytes, so the risk of leakage, overheating, or fire is much lower.
3. Are solid-state batteries commercially available now?
Only in limited or specialized applications. Large-scale commercial products—especially EV packs—are still in development.
4. How long do solid-state batteries last?
They typically offer a longer cycle life because the solid electrolyte is more stable and reduces internal degradation.
5. What industries will benefit most from solid-state batteries?
EVs, medical devices, aerospace, industrial sensors, and high-performance electronics where safety and energy density matter most.
6. Why are solid-state batteries more expensive?
Their materials and manufacturing methods are complex, and large-scale production has not yet been optimized.
7. Will solid-state batteries replace lithium-ion batteries?
Not immediately. They will likely enter niche and high-performance markets first, with broader adoption coming as production costs decrease.
Post time: Nov-24-2025