Key Highlights
Key Highlights
- Ni-MH industrial batteries are a dependable choice, offering a rechargeable battery solution for various applications.
- Their moderate to high energy density supports demanding industrial-grade Ni-MH uses.
- Nickel metal hydride technology ensures reduced environmental damage, distinguishing itself from older chemistries.
- These batteries are instrumental in sectors like medical devices, backup power systems, and hybrid electric vehicles.
- Improved designs have largely diminished the memory effect, enhancing both performance and longevity.
- Ni-MH batteries hold a commanding presence for specific industrial needs requiring stability and consistency.
Introduction
Today, the need for energy keeps changing fast. In this kind of world, Ni-MH industrial batteries are a reliable rechargeable battery choice. These nickel metal hydride batteries use nickel metal and metal hydride to give good energy density. This helps deliver the right amount of power if you need it in tough jobs. They are also strong and eco-friendly, so you can find them in many areas like medical technology and electric vehicles.
Ni-MH batteries are good because they deal well with problems like the memory effect. They last long, which makes them trusted by people who work in many fields. This is why these nickel metal hydride batteries are still the first choice for modern industrial needs. Now, let’s find out how the science behind them helps make them work so well.
Understanding Ni-MH Industrial Batteries
To truly appreciate the enduring value of industrial Ni-MH batteries, it’s essential to grasp their fundamental working principles and distinctive construction features.
Core Electrochemical Principles of Ni-MH Technology
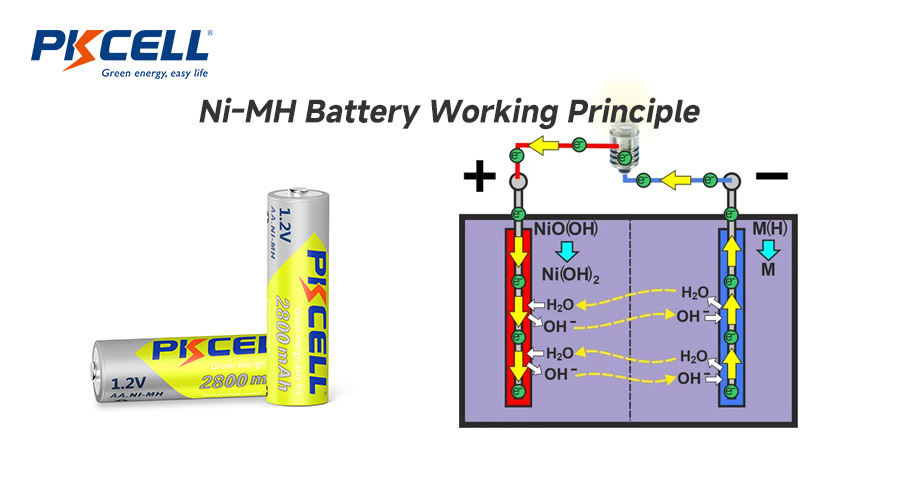
Ni-MH batteries work through reactions between nickel hydroxide and hydrogen-absorbing alloys. During charging, hydrogen ions move into the metal hydride, facilitated by potassium hydroxide. These parts work together to store and release energy, providing steady power and durability. The usual battery voltage in Ni-MH systems allows the electrolyte to facilitate ion movement during charging and discharge, maintaining a steady flow. Advances in compounds and electrode design reduce energy waste and improve power delivery, making Ni-MH batteries reliable for hybrid cars and backup systems.
What is the difference between Ni-MH industrial batteries and Ni-MH consumer batteries
| Feature | Ni-MH Industrial Battery | Ni-MH Consumer Battery |
| Primary Focus | Robustness, Reliability, and Performance for specific, demanding applications | Affordability, Convenience, and Standardization for everyday use |
| Construction | More durable materials, sturdier casings, superior sealing, often custom designs, or specific terminal configurations | Standardized sizes (AA, AAA, C, D, 9V), lighter, simpler construction for mass appeal under various conditions of use. |
| Current Handling | Engineered for higher continuous and peak discharge currents (e.g., power tools, HEVs) | Designed for moderate to high drain but generally lower current output compared to industrial counterparts |
| Temperature Range | Wider operating temperature range (e.g., -20°C to +60°C or beyond) with stable performance | Optimized for typical room temperatures, performance and lifespan are more susceptible to extremes |
| Cycle Life | Significantly longer cycle life due to higher-grade materials and construction, built for frequent, deep cycles | Good cycle life for consumer use (hundreds to over a thousand cycles), but typically less than industrial counterparts |
| Self-Discharge | Often incorporates Low Self-Discharge (LSD) technology as a standard feature, crucial for backup systems | Varies; some modern consumer batteries are LSD, but traditional ones may have higher self-discharge |
| Applications | Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV), Medical Devices, Industrial Backup Power, Telecommunications, Robotics, Power Tools, Security Systems | Digital Cameras, Flashlights, Remote Controls, Toys, Cordless Phones, Portable Audio Players |
| Safety & Certs | Subject to more stringent industrial safety standards (e.g., specific UL, IEC, UN38.3) and often part of systems with more robust BMS | Adheres to general safety standards but typically has less rigorous testing and simpler protection mechanisms than industrial |
| Cost & Value | Higher initial cost but offers lower total cost of ownership (TCO) due to extended lifespan and reliability in critical applications | Lower initial cost; provides good value for general consumer use but may have a shorter practical lifespan in heavy-use scenarios |
If you want to learn more about Ni-MH consumer batteries, just click on Top Benefits of Using Ni-MH Consumer Battery Today.
Where Industrial Ni-MH Batteries Excel: Key Applications
 Despite the rapid advancements of lithium-ion batteries, Ni-MH batteries, leveraging their specific performance advantages, continue to be a vital power solution in the following industrial applications:
Despite the rapid advancements of lithium-ion batteries, Ni-MH batteries, leveraging their specific performance advantages, continue to be a vital power solution in the following industrial applications:
Wireless Detector
- Reliable Power for Critical Sensing: Industrial wireless detectors, such as those used in security, environmental monitoring, or industrial process control, often operate in remote or harsh environments where reliable, long-lasting power is crucial.
- Core Advantage: Ni-MH batteries offer stable voltage output, robust performance across varying temperatures, and excellent safety characteristics. Their ability to handle intermittent high current draws (when transmitting data) combined with reliable low-drain standby, makes them ideal for these devices, ensuring uninterrupted data collection and security.
Medical Devices
- Life-Saving Assurance: Ni-MH batteries play a critical role in portable medical devices such as infusion pumps, portable monitors, respirators, and diagnostic equipment.
- Core Advantage: Medical devices demand extremely high levels of reliability, stability, and safety from their power sources. Ni-MH batteries’ relatively low risk of thermal runaway, stable voltage output, and good cycle life make them ideal for these life-sustaining or critical instruments. They ensure uninterrupted operation when it matters most, safeguarding patient well-being.
Industrial Backup Power Systems
- Uninterrupted Operation: In industrial control systems, telecommunications base stations, security systems, and emergency lighting, Ni-MH batteries are frequently employed as backup power sources (small-scale UPS).
- Core Advantage: They provide reliable instantaneous backup power, ensuring seamless system transition in the event of a main power outage. Ni-MH batteries maintain stable performance across a wide temperature range and are relatively easy to maintain, making them a dependable choice for demanding industrial environments.
Telecommunications Equipment
- Harsh Environment Adaptability: In remote telecommunications base stations, relay stations, or outdoor wireless network equipment, power reliability is paramount.
- Core Advantage: Ni-MH batteries are capable of withstanding significant temperature fluctuations and harsh outdoor conditions, providing consistent and reliable power support. Their robust construction and longer service life also contribute to reduced on-site maintenance frequency and costs.
Specialized Tools and Equipment
Ni-MH batteries give steady power to tools that need to work hard for long times.
- Alcohol sensor flashlights use Ni-MH batteries. This makes them run longer and work well even after long hours.
- Flashlights with Ni-MH batteries are easy to recharge. They keep working for a long time when you need them.
- If you use precision tools, Ni-MH helps them work the same way every time, even when the PAS voltage keeps changing.
These strong batteries last and help many kinds of tools that people use in tough jobs. The wide uses of Ni-MH batteries help make sure these tools perform well, even when the job is hard.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Industrial Ni-MH Batteries
In evaluating industrial Ni-MH batteries, understanding their strengths and weaknesses is crucial for making informed decisions.
Key Advantages
- High Safety: Ni-MH batteries boast a significantly lower risk of thermal runaway compared to lithium-ion, making them inherently more stable and less prone to explosion or combustion, crucial for safety-critical industrial uses.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Their initial manufacturing cost is typically lower than comparable lithium-ion batteries, offering a notable advantage for budget-conscious industrial projects.
- Environmental Friendliness: Free from highly toxic heavy metals like cadmium, lead, or mercury, Ni-MH batteries are more environmentally benign and easier to recycle than older battery chemistries.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range: Ni-MH batteries perform reliably across a broad temperature spectrum (typically -20°C to +60°C), making them ideal for challenging outdoor or fluctuating industrial environments.
- Higher Tolerance to Overcharge/Over-discharge: More forgiving than lithium-ion, Ni-MH batteries can tolerate some degree of overcharging and over-discharging, allowing for simpler battery management systems (BMS).
- High Reliability: As a mature and proven technology, Ni-MH batteries have a strong track record of high reliability across diverse industrial applications.
Noteworthy Disadvantages
Ni-MH batteries are useful, but they have some downsides:
- Memory effect: When you do not fully discharge them, it can hurt how long the battery lasts.
- Discharge limitations: Heavy use can make their voltage less steady.
- Temperature sensitivity: Very hot or cold weather makes them less efficient and harder to use everywhere.
- Charging duration: It often takes more time to charge them than some other battery types.
By knowing these problems, such as the memory effect, discharge issues, voltage drops, and slow charging, people can work on new ways to improve Ni-MH batteries. That helps them keep running strong in key systems.
Comparing Ni-MH with Other Industrial Battery Types
In industrial applications, selecting the appropriate battery technology is a critical decision. We will compare Ni-MH batteries with two other common competitors: lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries.
Ni-MH vs. Lithium-Ion: Strengths and Weaknesses
| Feature | Ni-MH | Lithium-ion |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 60-120 Wh/kg | 150-250 Wh/kg |
| Voltage Output | 1.2V stable | 3.0-3.7V drop |
| Cycle Durability | 500-1,500 cycles | 300-1,000 cycles |
| Cost Efficiency | $200/kWh | $350/kWh |
Ni-MH gives good long use for places that need strong and steady work. It is also a top pick when you want safety, as it stays stable over time. Lithium batteries are better for small tools or things you need to charge fast. When people think of energy density and voltage, they may find that lithium can give more in a small, light case, but you might pay more for it. Many like Ni-MH for steady power and safe charging, even when things get tough.
Ni-MH vs. Lead-Acid: Which Is More Suitable?
Ni-MH batteries do better than lead-acid ones when it comes to energy density, how many times you can use them, and their effect on the environment. Lead-acid batteries give a lot of volts, so they bring strong power for less money. But when it comes to using nickel metal hydride (Ni-MH) batteries, or Ni-MHyou need to ensure that your charger is compatible. Overall, you get a modern rechargeable battery with more lasting benefits.
Their smaller size lets you use nickel metal hydride batteries where you want it light and fast. If you want to save money and need a system for really tough jobs, lead-acid is still a good pick. In big jobs, what kind you use really depends on how big the project is and how much power you need.
Why Choose PKCELL When Buying Ni-MH Batteries?
When considering Ni-MH industrial batteries, PKCELL can be a solid choice due to their extensive manufacturing expertise spanning two decades and unwavering adherence to rigorous quality and safety standards. Our commitment to utilizing high-grade materials and optimized cell construction ensures that their Ni-MH industrial batteries deliver superior reliability, exceptional cycle life, and stable power output, even in demanding environments. PKCELL’s global presence and comprehensive range of certifications, including UL, IEC, CE, and RoHS, provide confidence in their product’s consistent performance and environmental compliance for diverse power needs, from telecommunications equipment to medical devices.
Conclusion
In short, Ni-MH industrial batteries are a good choice for many uses because they are strong and can do many jobs. You can see them in things like hybrid electric cars and as backup power for important systems. Their good points are often better than the bad points. To pick the best battery, it helps to know how they work and how they compare to other batteries, like lithium and lead-acid types. If you are looking at your choices for industrial batteries, think about the trust and smart use that PKCELL gives. For answers that fit what you need, contact us and get a quote today.
If you’re considering this battery for your project or need expert advice on the best solution, feel free to reach out for a free consultation. We’re here to help you choose the right power solution for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Ni-MH batteries safe for heavy-duty applications?
Yes, Ni-MH batteries are trusted for heavy-duty jobs. These batteries use nickel metal hydride, which lowers the heat risk. This makes them work well and safely every time. The metal hydride features help keep these batteries safe, strong, and long-lasting. That’s why nickel metal hydride rechargeable batteries are a good pick when you have work that needs both power and strength.
How do environmental factors affect Ni-MH battery performance?
Temperature and other environmental conditions can greatly affect how well a Ni-MH battery works. When you use them in a good temperature range, you get the best energy density, and the battery does not wear out as fast. If it gets too hot or too cold, it can become less reliable and harder to use after some time.
Post time: Jul-07-2025