What Do Modern Medical Health Devices Require from Their Batteries?
Compared with typical consumer electronics, medical devices impose far more stringent demands on their power source.
- Medical Devices commonly rely on stable voltage to ensure accurate operations.
- Many medical devices stay in standby mode and wake up several times a day. They need batteries that have a low self-discharge.
- Medical devices often touch the skin or stay on the body for long hours, so they need batteries to be safe. Batteries must withstand temperature changes, humidity, and everyday movement without swelling, leaking, or failing.
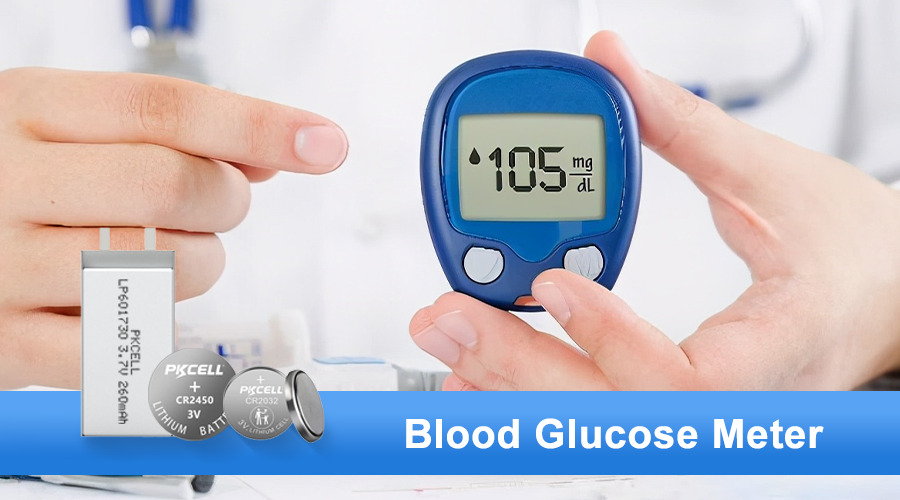
What are the Suitable Blood Glucose Batteries?
Handheld glucose meters usually operate in short bursts. Because of this intermittent usage, these meters commonly rely on non-rechargeable lithium coin cells, most often CR2032 or CR2450. These coin cells are ideal because they deliver a stable 3-volt output, have exceptionally long shelf life, and allow the device to work for months without replacement.
CGM devices, unlike traditional meters, need to transmit glucose readings to a smartphone or receiver every few minutes. This constant communication requires a small, lightweight, rechargeable power source.
The most common choice is a thin lithium-ion or lithium-polymer (LiPo) micro cell. These glucometer batteries are extremely light and can sit directly on the skin under an adhesive patch without causing discomfort. They also support the low-power Bluetooth and sensor electronics inside the transmitter.
The receiver or reader portion of the CGM system, which includes the screen and wireless communication, typically uses a larger rechargeable lithium battery—often in the 300–600mAh range.
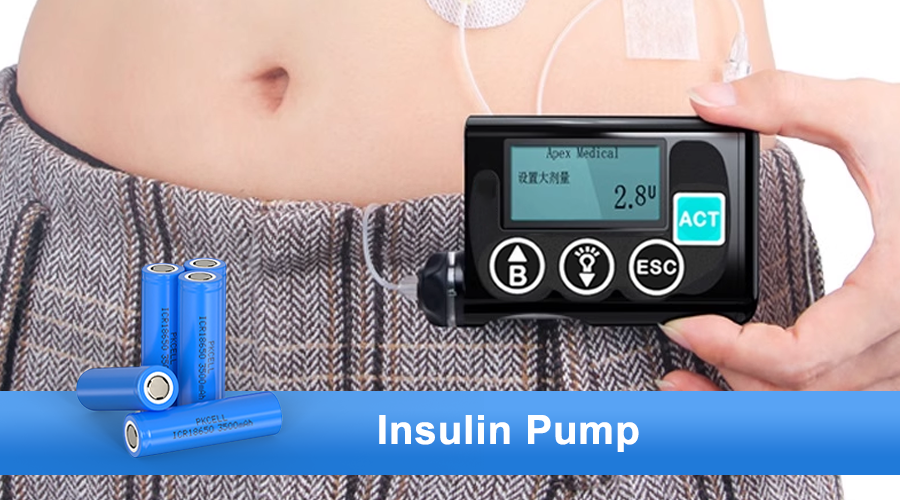
What Batteries Power Insulin Pump Models?
Some traditional pumps still rely on replaceable batteries, particularly AA or AAA lithium (Li-FeS₂) batteries. These lithium types are preferred because they are lighter than alkaline batteries, provide high pulse current, and maintain stable voltage across their discharge life.
They also perform well under temperature fluctuations, which is essential for a device worn against the body.
What Batteries Do Baby Monitor Cameras and Receivers Use?
Camera-based baby monitors typically rely on large rechargeable lithium-ion or LiPo battery packs, often between 1200mAh and 3000mAh. These cameras consume significant power due to video streaming, Wi-Fi connectivity, and infrared night vision.
Handheld parent units—the small monitors that parents carry around—usually use similar rechargeable lithium packs but at slightly lower capacities, often around 800mAh to 2000mAh.
Quote for Wholesale Prices of LiPo and Li-ion Battery
What Batteries Are Used in Baby Wearables and Skin-Contact Monitors?
Wearable infant monitors, such as breathing trackers or temperature patches, must remain small, soft, and safe.
The monitor batteries are usually tiny LiPo micro cells, ranging from 30mAh to 100mAh. Their soft-pack construction prevents hard edges from pressing into the baby’s skin, and they resist swelling even when exposed to body heat for long periods.
Because wearable baby products must run quietly and consistently, low self-discharge and stable voltage are essential characteristics.
What are the Most Suitable Digital Thermometer Batteries?
Older digital thermometers often rely on small alkaline or silver oxide button cells, such as LR41 or SR41. These batteries in the thermometer are low-cost, easy to replace, and sufficient for the short burst of power needed for a temperature reading.
Smart thermometers—especially those that transmit real-time data via Bluetooth—need rechargeable batteries. They often use very small lithium-ion micro batteries, typically around 20–50mAh.
How Should OEMs Choose the Right Battery for Their Medical Device?
- Choose the right battery shape: Because medical devices are becoming thinner and more ergonomic, the battery must conform to the shape of the product.
- Match the device’s operating cycle: Devices with occasional usage, like glucose meters, benefit from long-life coin cells. Devices with continuous operation, like insulin pumps, require rechargeable lithium chemistries with stable discharge curves.
- Meet Medical Safety Certifications
Most medical devices require multiple certifications such as: IEC 62133, UL1642, UN38.3 and CE / RoHS. A battery supplier with consistent chemistry and controlled manufacturing is essential for achieving these approvals.
Which Batteries Are Most Suitable for B2B Medical Device Manufacturing?
- Glucose meters commonly rely on CR2032 or CR2450 coin cells.
- CGM transmitters use thin rechargeable LiPo micro cells.
- CGM receivers and handheld monitors use larger rechargeable lithium-ion packs.
- Insulin pumps increasingly use custom LiPo packs designed for continuous operation.
- Baby monitor cameras rely on high-capacity Li-ion packs.
- Baby-wearable sensors use soft, thin LiPo micro cells.
- Smart thermometers prefer compact rechargeable Li-ion micro batteries.
Across the industry, the trend is moving steadily toward rechargeable lithium-polymer solutions, especially in devices involving wireless communication or continuous monitoring.
Why Choose PKCell?
For B2B medical device companies, partnering with a reliable battery manufacturer is essential. PKCell company offers long-term supply stability, customization ability, and strong safety compliance. Our lithium-ion batteries and Li-polymer batteries comply with international certificates like UN38.3, IEC, UL, etc.. PKCell also supports global delivery and competitive prices for bulk orders. If you need help choosing the right battery for your medical device, feel free to contact us.
Quote for Bulk PKCell Li-ion& Lipo Battery
Post time: Nov-19-2025